Nitric Oxide Synthase Jmol Tutorial
Introduction
Nitric Oxide Synthase enzymes (NOSs) catalyze the production of nitric oxide from arginine. This reaction is shown below. Reference
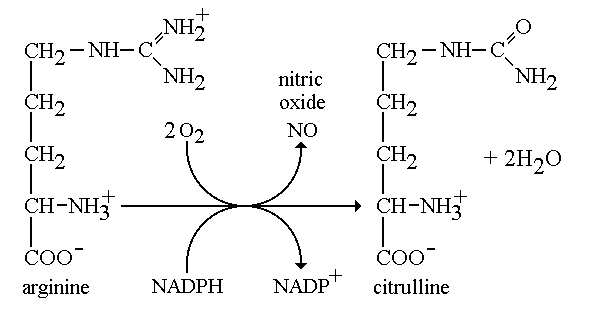
Nitric oxide (NO) is a colorless gas that is used for cellular signaling and for killing pathogens. It is produced continuously at low levels by cells and functions in tasks such the contraction of muscle cells and growth of nerve cells. Because it is a so small, NO rapidly diffuses, but at the same time, it stays relatively localized because it is highly reactive and rapidly inactivates. All of these properties make it an ideal messenger.
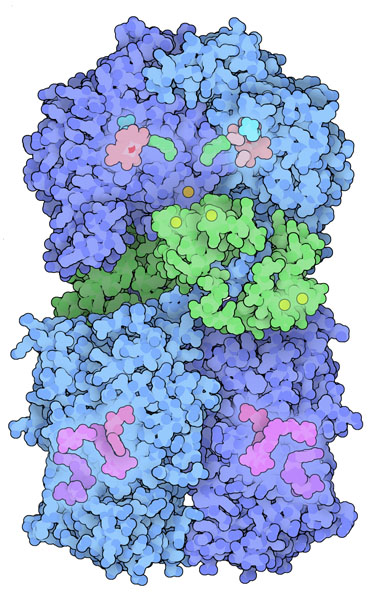
Mammalian cells have three isozymes of NOS: neuronal NOS (nNOS or NOS I), endothelial NOS (eNOS or NOS III) and inducible NOS (iNOS or NOSII). Neuronal NOS and endothelial NOS continually produce low levels of NO used for signaling. Inducible NOS, on the other hand, makes large toxic bursts of NO to fight pathogens. Neuronal NOS is illustrated on the right. Reference
Table of Contents
| Isozymes of
NOS |
Page 1 |
| Oxygenase
Domain |
Page 2 |
| Reductase
Domain |
Page 3 |
| Calmodulin
Binding Domain |
Page 4 |